12 unusual and early signs of blood clots
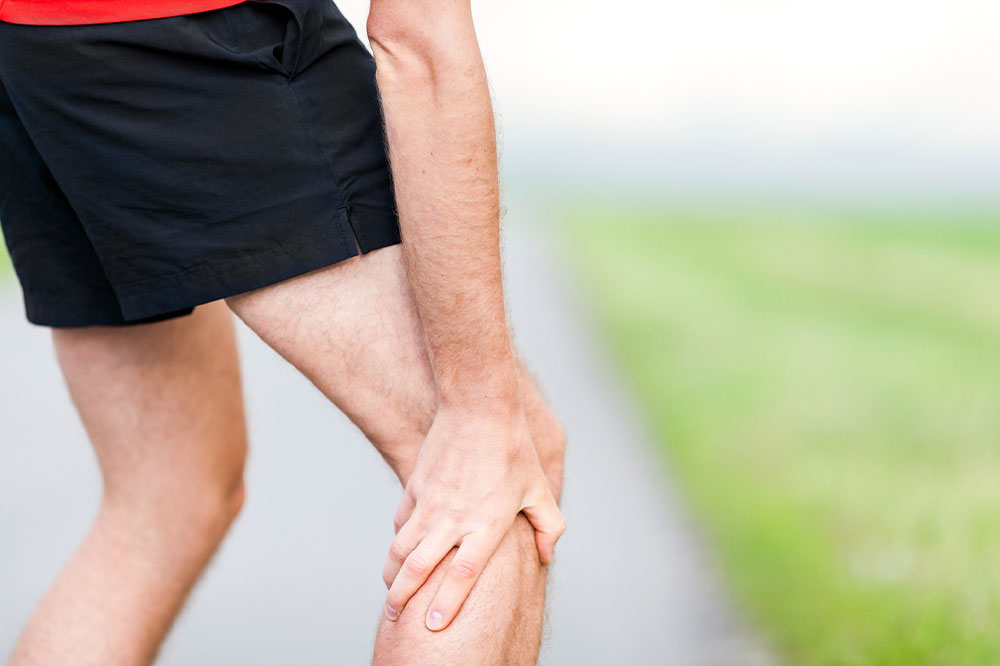

Circulation is one of the body’s critical functions, where freshly oxygenated blood from the lungs is pumped to all organs and extremities by the heart and is a continuous process. However, certain risk factors can trigger the formation of blood clots that affect this function. Several common and less typical signs make it difficult to confirm this problem. One should never ignore the early and unusual warning signs of blood clots.
Unexplained swelling
One of the earliest signs of a blood clot can be sudden and unexplained swelling in a specific body part. Blood flows through an intricate network of arteries and veins to all organs and extremities of the body. Clotting in this function results in the blood pooling that builds pressure and causes swelling. This type of swelling is easily identifiable as no injury or bruising results in the swelling.
Pain or tenderness
Blood clots often cause pain or tenderness in the affected area. Patients often complain about sudden cramps, a deep ache, or even a sharp stabbing pain that usually worsens with the most basic movements.
Warmth and redness
Clotting triggers a slight temperature change around the skin over a clot. It might feel warm to the touch and appear red or discolored. This is mainly due to increased blood flow and inflammation in the area.
Visible veins
Sometimes, one might notice the veins in the affected area becoming more prominent or visible. This can indicate a clot blocking normal blood flow, inflammation, and excessive swelling.
Skin discoloration
The skin in the blood clot area might also become discolored, appearing bluish or pale. This can be particularly noticeable in the extremities where a clot obstructs proper blood flow, depriving the organs of oxygen.
Difficulty breathing
Blood clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism) can cause sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that worsens with deep breaths, and trigger a rapid heart rate. This symptom requires immediate attention as it can result in respiratory and cardiovascular failure. Another sign of a pulmonary embolism is coughing up blood or having blood-tinged mucus.
Abdominal pain
A complication called mesenteric venous thrombosis can cause severe abdominal pain, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. This happens due to blood clots forming in the abdomen. The risk of this thrombosis is relatively rare but can be life-threatening if it develops unexpectedly.
Headaches and neurological symptoms
Blood also flows back and forth from the brain, and clotting in any part of the organ can result in cerebral venous thrombosis. This type of clot affects cognition, can lead to severe headaches, confusion, vision changes, and even cause seizures. The symptoms develop unexpectedly and may persist depending on the severity of the condition.
Unexplained fatigue
Blood carries fresh oxygen to all organs and extremities of the body. Clotting affects the flow and deprives the body of fresh oxygen in the affected areas. As a result, one will experience general fatigue and weakness, mainly if it is associated with other symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain.
Leg cramps
Although uncommon, persistent leg cramps, especially in the calf region, can sometimes indicate a blood clot. If these cramps develop unusually and exhibit erratic intensity or persistence, it’s essential to consider the possibility of a clot.
Localized fever
An area affected by a blood clot may feel warmer than the surrounding skin and increase body temperature, triggering a fever when the immune system is activated. This localized fever is due to inflammation in the clot-affected area.
Changes in skin texture
Visible changes in the skin are indicative of a developing blood clot. The skin might become increasingly tender and feel more firm or lumpy than the surrounding tissue.
Remember that these symptoms can vary in intensity and may be easily confused with other conditions. If one experiences any of these unusual warning signs, it is important to seek immediate attention. The risk factors for blood clots worsen with a history of clotting disorders, recent surgery, prolonged immobility, or a family history indicative of genetic conditions resulting from the clot. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent potentially severe complications associated with blood clots. One must also follow an active lifestyle and a healthy meal plan to manage the abovementioned symptoms better.