5 Conditions That Can Trigger Hair Loss
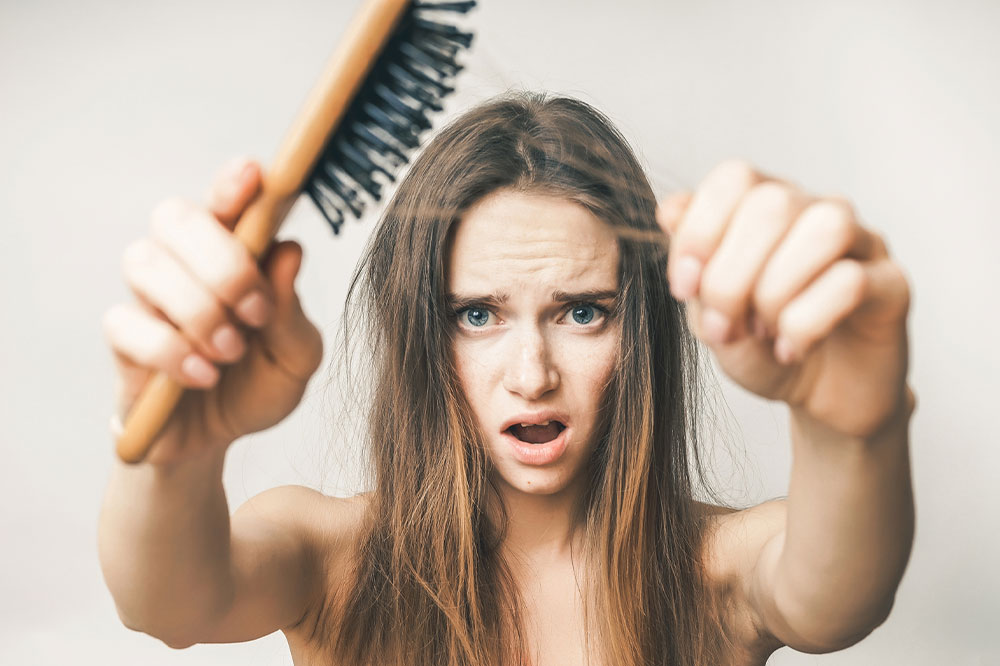

Hair loss is a universal problem that affects many people. While some amount of hair loss is normal and is brought on by age, lifestyle, or genetics, severe hair loss may indicate an underlying health condition. Further, treating the condition can, at times, help reduce hair loss or stop it from worsening. Here are a few conditions that can trigger the loss of hair and the management options to deal with it:
Understanding hair loss
While there is no permanent cure for hair loss, certain treatment options and therapeutic measures can help manage the condition. Many may experience mild to moderate hair loss at some point, but severe hair loss is a much more serious condition requiring treatment. The prognosis for someone who experiences severe hair loss depends on the degree of damage. If one loses a significant amount of hair, it may be difficult to reverse the damage. However, scalp treatments, supplements, surgery, or hair transplant can help restore hair growth. If the cause is unknown or if hair remains unaffected by treatment, doctors may be unable to predict a clear outcome. Here, seeking psychological support may be necessary to help manage the emotional impact of hair loss. In any case, it is essential to consult a doctor to understand the cause of hair loss and explore the best treatment options. With proper care and support, one can manage the condition and restore hair growth to a certain extent.
Conditions that trigger hair loss
While usually not a serious concern in itself, losing hair can cause significant psychological stress. Further, hair loss can indicate poor health or existing conditions. Here are a few health conditions that can trigger hair loss:
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that results in bald patches on the scalp and other parts of the body. The exact cause of this condition is not known, but it is believed to be linked to genetics, stress, and environmental factors.
Management options: When it comes to alopecia areata treatments, one can find many options, ranging from topical treatments like creams or lotions that help slow down or stop hair loss to supplements that can help promote hair growth. Additionally, doctors may recommend light therapy and immunotherapy as treatment options for alopecia areata. Further, lifestyle changes such as stress management and following a balanced meal plan may also benefit those dealing with alopecia areata. However, seeking emotional support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals is essential, as this condition can take an emotional toll. With the right combination of treatments and lifestyle changes, alopecia areata can be managed.
Anemia
Anemia is characterized by a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the body, resulting in fatigue and other symptoms. While there are many types of anemia, the most common is iron deficiency anemia, which develops when the body does not get enough iron to produce hemoglobin. Hair loss is a common symptom of anemia, as the lack of oxygen to the hair follicles can cause them to weaken and fall out. Sometimes, anemia-related hair loss can be severe, with significant hair thinning and bald spots. Fortunately, it is usually reversible if the underlying anemia is treated.
Management options: The most crucial step in treating anemia-related hair loss is identifying and treating the underlying cause. If the anemia is brought on by iron deficiency, doctors will likely recommend increasing the intake of iron-rich foods such as red meat, fish, spinach, and beans. Additionally, they may prescribe iron supplements or vitamin B12 shots to help increase red blood cell count. In more severe cases, blood transfusions or other supplements may be required to treat the anemia.
Lupus
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can cause severe hair loss. Here, the body’s immune system attacks healthy cells and tissues, leading to inflammation. Lupus can cause hair follicles to become damaged or stop producing hair. The most common symptoms of lupus are joint pain, fatigue, rashes, fever, and extreme sun sensitivity. Hair loss is a less common, yet likely, symptom of the condition.
Management options: Treatments for lupus-related hair loss include prescriptions that suppress the immune system. These options can reduce inflammation and help prevent further damage to the hair follicles. It is important to note that while treatment can help reduce the effects of lupus-related hair loss, there is no cure for the condition itself. Living with lupus may require long-term management of symptoms and healthcare.
Telogen effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a type of hair loss that develops due to a disruption in the normal growth cycle of the hair. It is characterized by a sudden, widespread thinning of hair on the scalp. This can be triggered by stress, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, treatment options, and illness. Here, more hair follicles than usual enter the telogen (resting) phase of the cycle, eventually falling out or becoming thinner. Fortunately, telogen effluvium is generally temporary, and its effects are typically reversed with time. In some cases, however, there may be some permanent hair loss.
Management options: When dealing with telogen effluvium, in addition to prescription options, lifestyle changes (such as stress management and better nutrition) and supplements can stimulate new hair growth.
Thyroid disease
Thyroid disease occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much or too little hormones. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) may lead to thinning hair and even baldness, while an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can cause hair to fall out rapidly. If one observes sudden or severe hair loss along with changes in energy levels and body temperature, they should consider consulting a doctor regarding thyroid health.
Management options: Treatment for thyroid-related hair loss depends on the underlying cause. If the hair loss is triggered by hypothyroidism, hormone therapy may be recommended. On the other hand, if hair loss is caused by hyperthyroidism, supplements may be prescribed. Additionally, topical creams, shampoos, and light therapy may help manage the disease.
One should consult a doctor to understand the side effects before initiating any treatment.