Early warning signs of amyloidosis to be aware of
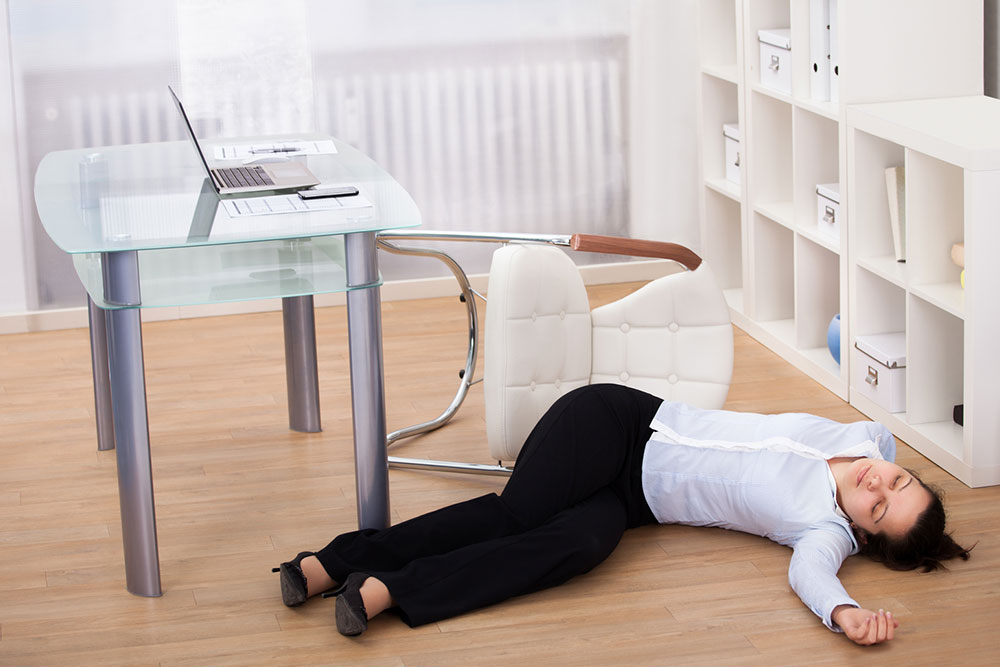

Amyloidosis is a rare and intricate health condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal amyloid proteins in various organs and tissues throughout the body. Due to its infrequency and the often subtle nature of its symptoms, diagnosing amyloidosis in its early stages can be a formidable challenge. Nevertheless, early detection is paramount for effective management and treatment. Here’s a look into the crucial early warning signs of amyloidosis that individuals should remain vigilant about.
Fatigue and weakness
Unexplained fatigue and weakness often serve as the initial signs of amyloidosis. As amyloid proteins accumulate in different organs, they can disrupt regular bodily functions, leading to persistent feelings of weariness and weakness.
Swelling of ankles and legs
Amyloidosis can impact the heart, resulting in a condition called restrictive cardiomyopathy. This can also cause fluid retention and swelling, which is often observed in the ankles and legs. Unexplained swelling should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare professional.
Shortness of breath
With the accumulation of amyloid deposits in the heart and lungs, individuals grappling with amyloidosis may experience shortness of breath, particularly during physical exertion. This symptom can be mistaken for other respiratory issues, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis.
Irregular heartbeat
Amyloidosis can interfere with the heart’s normal electrical signaling, leading to arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats. Palpitations, dizziness, or fainting episodes may occur. Vigilant monitoring of heart rhythm becomes pivotal in cases of suspected amyloidosis.
Numbness or tingling
Amyloid deposits can affect the nerves, resulting in peripheral neuropathy. This can manifest as numbness, tingling, and a sensation akin to “pins and needles” in the extremities. In such cases, it is important to pay attention to the unexplained neurological symptoms.
Low BMI and poor appetite
Unexplained reduction in BMI levels and a diminished appetite are subtle yet significant early manifestations of amyloidosis. As the condition progresses, it can interfere with digestion and nutrient absorption, culminating in a drastic reduction in BMI.
Skin changes
Certain individuals grappling with amyloidosis may notice skin alterations, including a waxy appearance or purplish patches known as petechiae. These skin irregularities can provide vital clues regarding underlying amyloid deposits.
Enlarged liver or spleen
Amyloidosis can prompt the enlargement of the liver or spleen, potentially detectable during a physical examination. Enlargement of these organs can induce discomfort and necessitates evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Thickened tongue or hoarseness
Amyloid deposits can accumulate in the tongue and vocal cords, resulting in a thickened tongue or hoarseness in the voice. Changes in speech or difficulties in swallowing may also surface.
Gastrointestinal symptoms
Amyloidosis can influence the gastrointestinal tract, leading to symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, or the presence of blood in the stool. If these digestive issues occur along with the other symptoms of amyloidosis, it is crucial to consult a primary care doctor.
Bone pain
As amyloid deposits accumulate in bone marrow, individuals with amyloidosis may experience bone pain, which can be persistent and intensify over time. This pain can affect various parts of the body.
Enlarged lymph nodes
Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes, typically detected in the neck, armpits, or groin, can be associated with amyloidosis. While lymph node enlargement can occur for various reasons, it should not be overlooked.
Vision changes
In rare cases, amyloidosis can affect the eyes, leading to vision changes such as blurred vision, difficulty focusing, or increased sensitivity to light. Any unexplained changes in vision should be assessed by an eye specialist.
Heart murmurs
Amyloidosis’s impact on the heart can result in heart murmurs, which are abnormal sounds detected during a physical examination. Healthcare professionals should further investigate the presence of heart murmurs if a person is at a known risk of this condition.
Swallowing difficulties
As amyloids accumulate in the throat and esophagus, affected individuals may experience difficulty swallowing, a sensation of something being stuck in the throat, or discomfort while eating.
Kidney dysfunction
Amyloid deposits can impair kidney function, leading to proteinuria (excess protein in the urine), edema (fluid retention), and changes in urine color or frequency. Kidney function tests are essential in evaluating amyloidosis.
Low blood pressure
Amyloidosis can disrupt the autonomic nervous system, leading to orthostatic hypotension—a significant drop in blood pressure upon standing. This can cause fainting or dizziness.
Swollen salivary glands
In some cases, amyloidosis can cause swelling of the salivary glands, leading to discomfort, dry mouth, and difficulty with speech and swallowing.
Amyloidosis, though rare, is a condition that demands vigilance. Recognizing its early warning signs is vital for timely diagnosis and subsequent treatment. If one is experiencing any of these symptoms, especially when they persist or intensify, prompt consultation with a healthcare professional remains essential.